
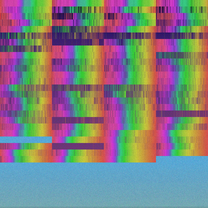
Absorption spectra for the chemical elements 1 - 128, using actual nist data. The spectral colors are approximate; feel free to try and improve on that. Made with help from Chatgpt and Google Colab.
#!/usr/bin/env python3 """ generate_spectra.py Generate a 4096×4096-pixel image of the absorption spectra for elements Z=1–128,\ laid out in 4 columns × 32 rows, using every 24-bit RGB color exactly once. - Absorption lines from NIST (380–780 nm) are drawn with the darkest colors. - Background for known-spectrum tiles is a smooth gradient ordered from violet→blue→green→yellow→orange→red, applied individually, right-to-left. - Background for unknown-spectrum tiles (no NIST data) is flat gray. Dependencies: pip install astroquery astropy pillow numpy pandas """ import numpy as np from PIL import Image from astroquery.nist import Nist from astropy import units as u import pandas as pd # --- 1. Setup --- tile_w, tile_h = 1024, 128 ncols, nrows = 4, 32 width, height = tile_w * ncols, tile_h * nrows total_pixels = width * height print(f"Total pixels: {total_pixels}") # Atomic symbols Z=1–118 element_symbols = [ 'H','He','Li','Be','B','C','N','O','F','Ne', 'Na','Mg','Al','Si','P','S','Cl','Ar','K','Ca', 'Sc','Ti','V','Cr','Mn','Fe','Co','Ni','Cu','Zn', 'Ga','Ge','As','Se','Br','Kr','Rb','Sr','Y','Zr', 'Nb','Mo','Tc','Ru','Rh','Pd','Ag','Cd','In','Sn', 'Sb','Te','I','Xe','Cs','Ba','La','Ce','Pr','Nd', 'Pm','Sm','Eu','Gd','Tb','Dy','Ho','Er','Tm','Yb', 'Lu','Hf','Ta','W','Re','Os','Ir','Pt','Au','Hg', 'Tl','Pb','Bi','Po','At','Rn','Fr','Ra','Ac','Th', 'Pa','U','Np','Pu','Am','Cm','Bk','Cf','Es','Fm', 'Md','No','Lr','Rf','Db','Sg','Bh','Hs','Mt','Ds', 'Rg','Cn','Nh','Fl','Mc','Lv','Ts','Og' ] # --- 2. Fetch NIST spectral lines --- spectral_lines = {} nist = Nist() for Z, sym in enumerate(element_symbols, start=1): try: table = nist.query(380*u.nm, 780*u.nm, linename=sym) df = table.to_pandas() if table is not None else pd.DataFrame() if 'Observed' in df.columns: col = df['Observed'] elif 'Ritz' in df.columns: col = df['Ritz'] elif 'Wavelength' in df.columns: col = df['Wavelength'] else: spectral_lines[Z] = [] continue vals = pd.to_numeric(col, errors='coerce').dropna().astype(float) if len(vals) and vals.max() > 1000: vals /= 10.0 spectral_lines[Z] = [w for w in vals if 380 <= w <= 780] except Exception as e: print(f"Warning Z={Z} fetch: {e}") spectral_lines[Z] = [] # Classify known vs unknown known_ids = [Z for Z in range(1,129) if spectral_lines.get(Z)] unknown_ids = [Z for Z in range(1,129) if Z not in known_ids] print(f"Known spectra: {len(known_ids)}, Unknown: {len(unknown_ids)}") # --- 3. Sort all colors by brightness --- colors = np.arange(total_pixels, dtype=np.uint32) R = (colors >> 16) & 0xFF G = (colors >> 8) & 0xFF B = colors & 0xFF brightness = 0.299*R + 0.587*G + 0.114*B sorted_idx = np.argsort(brightness) # darkest-first # --- 4. Identify line pixels and counts --- y = np.arange(total_pixels)//width x = np.arange(total_pixels)%width tile_row = y//tile_h tile_col = x//tile_w tile_id = tile_row*ncols + tile_col + 1 line_pixels = [] for Z in known_ids: r, c = divmod(Z-1, ncols) y0, x0 = r*tile_h, c*tile_w for wl in spectral_lines[Z]: xi = x0 + int((wl-380)/400*(tile_w-1)) ys = np.arange(y0, y0+tile_h) line_pixels.extend((ys*width + xi).tolist()) line_flat = np.unique(np.array(line_pixels, dtype=np.int64)) M = len(line_flat) print(f"Absorption line pixels: {M}") # --- 5. Background counts --- mask_unk_bg = (~np.isin(np.arange(total_pixels), line_flat)) & np.isin(tile_id, unknown_ids) G_count = mask_unk_bg.sum() R_count = total_pixels - M - G_count print(f"Gray: {G_count}, Rainbow: {R_count}") assert M + G_count + R_count == total_pixels # --- 6. Build color pools --- line_pool = sorted_idx[:M] remaining = sorted_idx[M:] # Gray pool grayness = np.abs((remaining>>16)&0xFF - (remaining>>8)&0xFF) + \ np.abs((remaining>>8)&0xFF - (remaining&0xFF)) + \ np.abs((remaining>>16)&0xFF - (remaining&0xFF)) g_idx = np.argsort(grayness)[:G_count] gray_pool = remaining[g_idx] # Rainbow pool rainbow_pool = np.delete(remaining, g_idx) print(f"Pools: lines={len(line_pool)}, gray={len(gray_pool)}, rainbow={len(rainbow_pool)}") # --- 7. Assign pixels --- img_flat = np.zeros((total_pixels,3), dtype=np.uint8) # Lines gc = line_pool img_flat[line_flat] = np.stack([((gc>>16)&0xFF),((gc>>8)&0xFF),(gc&0xFF)],1) # Gray backgrounds ug = np.where(mask_unk_bg)[0] gc = gray_pool img_flat[ug] = np.stack([((gc>>16)&0xFF),((gc>>8)&0xFF),(gc&0xFF)],1) # Rainbow backgrounds per element reversed gradient # Compute HSV hue and sort rainbow_pool by hue R3 = R[rainbow_pool]/255.0; G3 = G[rainbow_pool]/255.0; B3 = B[rainbow_pool]/255.0 maxc = np.maximum.reduce([R3, G3, B3]); minc = np.minimum.reduce([R3, G3, B3]); diff = maxc - minc hue = np.zeros_like(maxc) maskv = diff > 1e-6 rm = maskv & (maxc == R3); gm = maskv & (maxc == G3); bm = maskv & (maxc == B3) hue[rm] = (60 * ((G3[rm] - B3[rm]) / diff[rm]) + 360) % 360 hue[gm] = (60 * ((B3[gm] - R3[gm]) / diff[gm]) + 120) % 360 hue[bm] = (60 * ((R3[bm] - G3[bm]) / diff[bm]) + 240) % 360 hue_norm = hue / 360.0 hue_order = np.argsort(hue_norm) rainbow_sorted = rainbow_pool[hue_order] # Modular interleaving & duplicate resolution n = len(rainbow_sorted); k = len(known_ids) tile_positions = {} for idx, Z in enumerate(known_ids): count = np.count_nonzero((~np.isin(np.arange(total_pixels), line_flat)) & (tile_id == Z)) pos = (np.arange(count) * k + idx) % n tile_positions[Z] = pos.tolist() all_pos = sum(tile_positions.values(), []) unique_pos, counts = np.unique(all_pos, return_counts=True) dupes = unique_pos[counts > 1] missing = list(set(range(n)) - set(unique_pos)) def resolve_dupes(tile_positions, counts_map, missing): for Z in known_ids: lst = tile_positions[Z] for i, p in enumerate(lst): if counts_map[p] > 1 and missing: newp = missing.pop() counts_map[p] -= 1 counts_map[newp] = 1 lst[i] = newp if not missing: break counts_map = {p: c for p, c in zip(unique_pos, counts)} resolve_dupes(tile_positions, counts_map, missing) # Assign per-element reversed gradient for Z in known_ids: pos = np.array(tile_positions[Z], dtype=int) cols = rainbow_sorted[pos] local_h = hue_norm[hue_order][pos] grad_idx = np.argsort(local_h) cols_sorted = cols[grad_idx] # reverse for right-to-left gradient cols_sorted = cols_sorted[::-1] mask_k = (~np.isin(np.arange(total_pixels), line_flat)) & (tile_id == Z) idxs = np.where(mask_k)[0] # assign to pixels sorted by x-coordinate order_x = np.argsort(idxs % width) img_flat[idxs[order_x]] = np.stack([((cols_sorted>>16)&0xFF),((cols_sorted>>8)&0xFF),(cols_sorted&0xFF)],1) # --- 8. Save image --- print("Saving image...") Image.fromarray(img_flat.reshape((height, width, 3))).save('absorption_spectra.png') print('Done.')
| Date | |
|---|---|
| Colors | 16,777,216 |
| Pixels | 16,777,216 |
| Dimensions | 4,096 × 4,096 |
| Bytes | 48,693,692 |
