
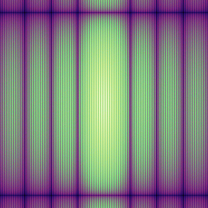
Inspired by results observed with double-slit experiments. Made with Chatgpt 5, Python 3, and a Google Colab notebook.
#!/usr/bin/env python3 """ AllRGB + Physics: Fraunhofer double-slit diffraction, 4096×4096, using each 24-bit RGB color exactly once. Model: I(x,y) ∝ cos^2(π x / Δx_interf) · sinc^2(x / Δx_env_x) · sinc^2(y / Δx_env_y) where np.sinc(z) = sin(πz)/(πz) ⇒ sinc(α) with α = π x/Δ becomes np.sinc(x/Δ). Brightness mapping: - Sort pixels by physical intensity I (dark → bright). - Sort all 16,777,216 RGB colors by Rec.709 relative luminance Y=0.2126R+0.7152G+0.0722B (dark → bright). - Pair ranks 1:1 to preserve monotone brightness, guaranteeing exact once-only color usage. References: - Fraunhofer diffraction & rectangular aperture (sinc²): Wikipedia (Fraunhofer diffraction equation; Rectangular aperture section). - Double-slit factor cos²×sinc²: standard optics notes/Q&A. - Rec.709 luminance coefficients (also sRGB primaries): ITU-R BT.709 / Luma (video) page. Citations are provided in the chat response. """ import numpy as np from PIL import Image from datetime import datetime # ------------------------------ CONFIG ------------------------------ W = H = 4096 # Physical-pattern knobs (in PIXELS of the observation plane): # First zeros of the single-slit envelopes (controls the sinc² widths). FIRST_ZERO_X = 520.0 # pixels to first horizontal minimum (∝ λR / slit_width) FIRST_ZERO_Y = 1800.0 # pixels to first vertical minimum (∝ λR / slit_height) # Interference fringe spacing (distance between cos² maxima). FRINGE_SPACING = 44.0 # pixels between bright fringes (∝ λR / slit_separation) # Gamma to gently compress dynamic range of intensity before mapping. INTENSITY_GAMMA = 1.0 # 1.0 = no change; >1 brightens midtones, <1 darkens # Output filename STAMP = datetime.now().strftime("%Y%m%d_%H%M%S") OUT_PNG = f"allrgb_fraunhofer_double_slit_{W}x{H}_{STAMP}.png" # ------------------------------ PHYSICS FIELD ------------------------------ def fraunhofer_double_slit_intensity(w=W, h=H, first_zero_x=FIRST_ZERO_X, first_zero_y=FIRST_ZERO_Y, fringe_px=FRINGE_SPACING, gamma=INTENSITY_GAMMA): """ Build a physically faithful far-field intensity for a finite-height double slit. I(x,y) ∝ cos^2(π x / fringe_px) · sinc^2(x / first_zero_x) · sinc^2(y / first_zero_y) Using np.sinc(z) = sin(πz)/(πz) so sinc(π x/Δ)/(π x/Δ) == np.sinc(x/Δ). Returns ------- I : float32 array, shape (h, w), normalized to [0,1]. """ y = np.arange(h, dtype=np.float32) - (h - 1) / 2.0 x = np.arange(w, dtype=np.float32) - (w - 1) / 2.0 X, Y = np.meshgrid(x, y) # Interference (two coherent slits separated along x) cos2 = np.cos(np.pi * X / float(fringe_px)) ** 2 # Finite slit width/height envelopes (rectangular apertures) env_x = np.sinc(X / float(first_zero_x)) ** 2 env_y = np.sinc(Y / float(first_zero_y)) ** 2 I = cos2 * env_x * env_y if gamma != 1.0: # Optional tone shaping, still monotone I = I ** (1.0 / float(gamma)) # Normalize robustly I -= I.min() m = I.max() if m > 0: I /= m return I.astype(np.float32, copy=False) # ------------------------------ COLOR ORDERING ------------------------------ def colors_sorted_by_rec709_luma(): """ Generate all 24-bit colors exactly once and return their channels sorted by Rec.709 relative luminance (dark -> bright). Returns ------- Rs, Gs, Bs : uint8 arrays of length N=W*H, luminance-sorted. """ N = W * H c = np.arange(N, dtype=np.uint32) # packed RGB as 0xRRGGBB R = ((c >> 16) & 0xFF).astype(np.float32) G = ((c >> 8) & 0xFF).astype(np.float32) B = ( c & 0xFF).astype(np.float32) # Rec.709 relative luminance (linear light) Y = 0.2126 * R + 0.7152 * G + 0.0722 * B order = np.argsort(Y, kind="stable") # deterministic & monotone Rs = R[order].astype(np.uint8, copy=False) Gs = G[order].astype(np.uint8, copy=False) Bs = B[order].astype(np.uint8, copy=False) # Free intermediates del R, G, B, Y, order, c return Rs, Gs, Bs # ------------------------------ ASSEMBLY & CHECKS ------------------------------ def assemble_and_verify(I, Rs, Gs, Bs, out_path=OUT_PNG): """ Rank-match intensity to luminance and write PNG. Also verifies exact once-only 24-bit coverage via multiple invariants. """ N = I.size pix_order = np.argsort(I.ravel(), kind="stable") img_flat = np.empty((N, 3), dtype=np.uint8) img_flat[pix_order, 0] = Rs img_flat[pix_order, 1] = Gs img_flat[pix_order, 2] = Bs del Rs, Gs, Bs, pix_order img = img_flat.reshape((H, W, 3)) del img_flat packed = (img[...,0].astype(np.uint32) << 16) | \ (img[...,1].astype(np.uint32) << 8) | \ (img[...,2].astype(np.uint32) ) exp = np.arange(N, dtype=np.uint32) got_sum = int(packed.sum(dtype=np.uint64)) exp_sum = int(exp.sum(dtype=np.uint64)) got_sum2 = int((packed.astype(np.uint64) * packed.astype(np.uint64)).sum(dtype=np.uint64)) exp_sum2 = int((exp.astype(np.uint64) * exp.astype(np.uint64)).sum(dtype=np.uint64)) # FIXED: flatten before XOR reduce so we get a scalar got_xor = int(np.bitwise_xor.reduce(packed.ravel().astype(np.uint32))) exp_xor = int(np.bitwise_xor.reduce(exp)) assert got_sum == exp_sum and got_sum2 == exp_sum2 and got_xor == exp_xor, \ "Color coverage mismatch — not a perfect permutation of all 24-bit colors." Image.fromarray(img, mode="RGB").save(out_path, optimize=True) print(f"Saved: {out_path}") def main(): print(f"Image: {W}×{H} (pixels: {W*H:,})") print("Computing Fraunhofer double-slit intensity field…") I = fraunhofer_double_slit_intensity() print("Ranking all 16,777,216 colors by Rec.709 luminance…") Rs, Gs, Bs = colors_sorted_by_rec709_luma() print("Assembling output image with exactly-once color coverage…") assemble_and_verify(I, Rs, Gs, Bs, out_path=OUT_PNG) if __name__ == "__main__": # Be reproducible and concise in NumPy prints np.set_printoptions(suppress=True) main()
| Date | |
|---|---|
| Colors | 16,777,216 |
| Pixels | 16,777,216 |
| Dimensions | 4,096 × 4,096 |
| Bytes | 49,616,095 |
